Acklins and Crooked Islands
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2014) |
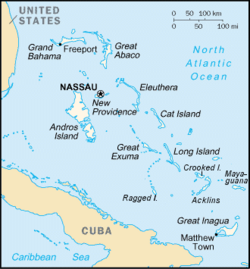
Acklins and Crooked Islands was a district of the Bahamas until 1996, and as Acklins, Crooked Island and Long Cay until 1999. (islands are located at 22°30′N 74°0′W / 22.500°N 74.000°W)[1]
It consisted of a group of islands semi-encircling a large, shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins, of which the largest are Crooked Island in the north and Acklins in the south-east, and the smaller are Long Cay (once known as Fortune Island) in the north-west, and Castle Island in the south.[2][3]
The islands were settled by American Loyalists in the late 1780s who set cotton plantations employing over 1,000 slaves. After the abolition of slavery in the British Empire these became uneconomical, and the replacement income from sponge diving has now dwindled as well. The inhabitants now live by fishing and small-scale farming.
The main town in the group is Colonel Hill on Crooked Island. Albert Town, on Long Cay, now sparsely populated, was once a prosperous little town. It was engaged in the sponge and salt industries and also served as a transfer port for stevedores seeking work on passing ships.
The population of Acklins was 428, and Crooked Island 350, at the 2000 census.
Since 1999, Acklins and Crooked Island are separate districts.
References
[edit]- ^ Crooked Island, Texas A&M University at Galveston, Retrieved November 6, 2013
- ^ Bahamas Out Islands: Acklins and Crooked Islands, Retrieved November 6, 2013
- ^ Acklins Crooked Island, Geographia.com, Retrieved November 6, 2013
